
Clinical Trials for PNH
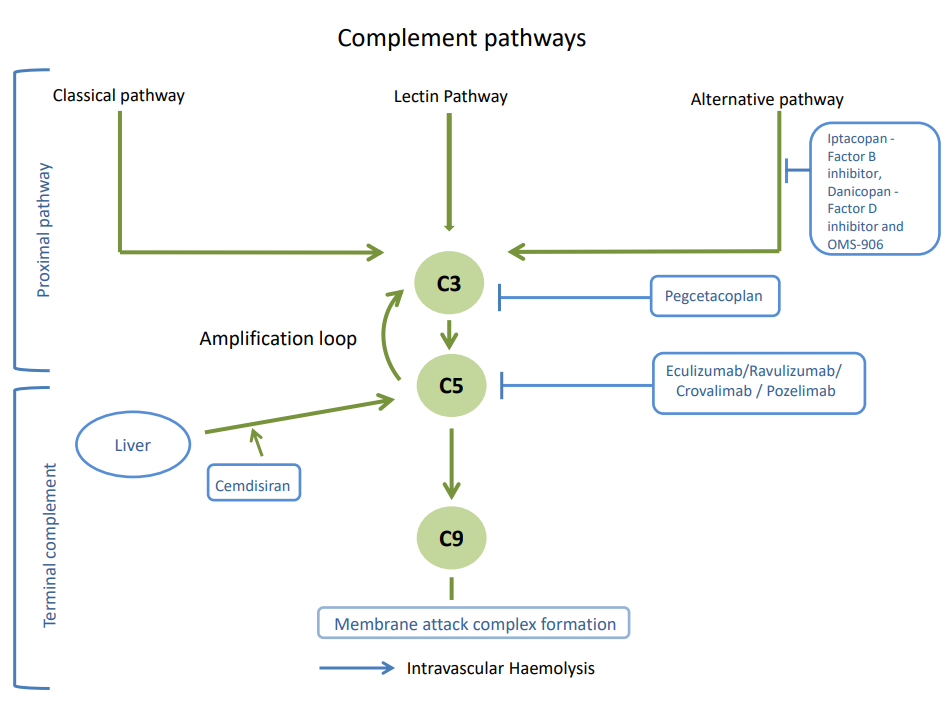
Treatment for PNH has progressed significantly in the last 20 years. We are now in a position to look at optimising treatment for patients in terms of the modality of treatment and managing anaemia for patients experiencing extravascular haemolysis.
The National PNH Service has clinical trials currently open (Leeds, King’s and Monklands) for patients who are new to treatment and those already on treatment with Eculizumab or Ravulizumab. These include self-injection infusions or short injections, oral treatments or a combination of intravenous or oral treatments.
We aim to offer all patients with PNH who are eligible for a clinical trial option for them to consider, and this will be discussed at clinic appointments.
| Trial Name | Trial Target | Method of Application | Leeds | London | Monklands |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALXN 303 | C5 inhibitor treated patients – Factor D inhibitor add-on | Oral | Closed | Closed | N/A |
| Novartis Apply | Eculizumab treated patient – proximal complement inhibitor | Oral | Closed | Closed | N/A |
| Regeneron 2021 | Naive patients – C5 inhibitor and SiRNA | Subcutaneous injection | Open | N/A | N/A |
| Omeros | C5 inhibitor treated patients – proximal complement inhibitor | Intravenous | Closed | Closed | N/A |
| Novartis Appulse | C5 inhibitor treated patients – proximal complement inhibitor | Oral | Closed | N/A | N/A |
